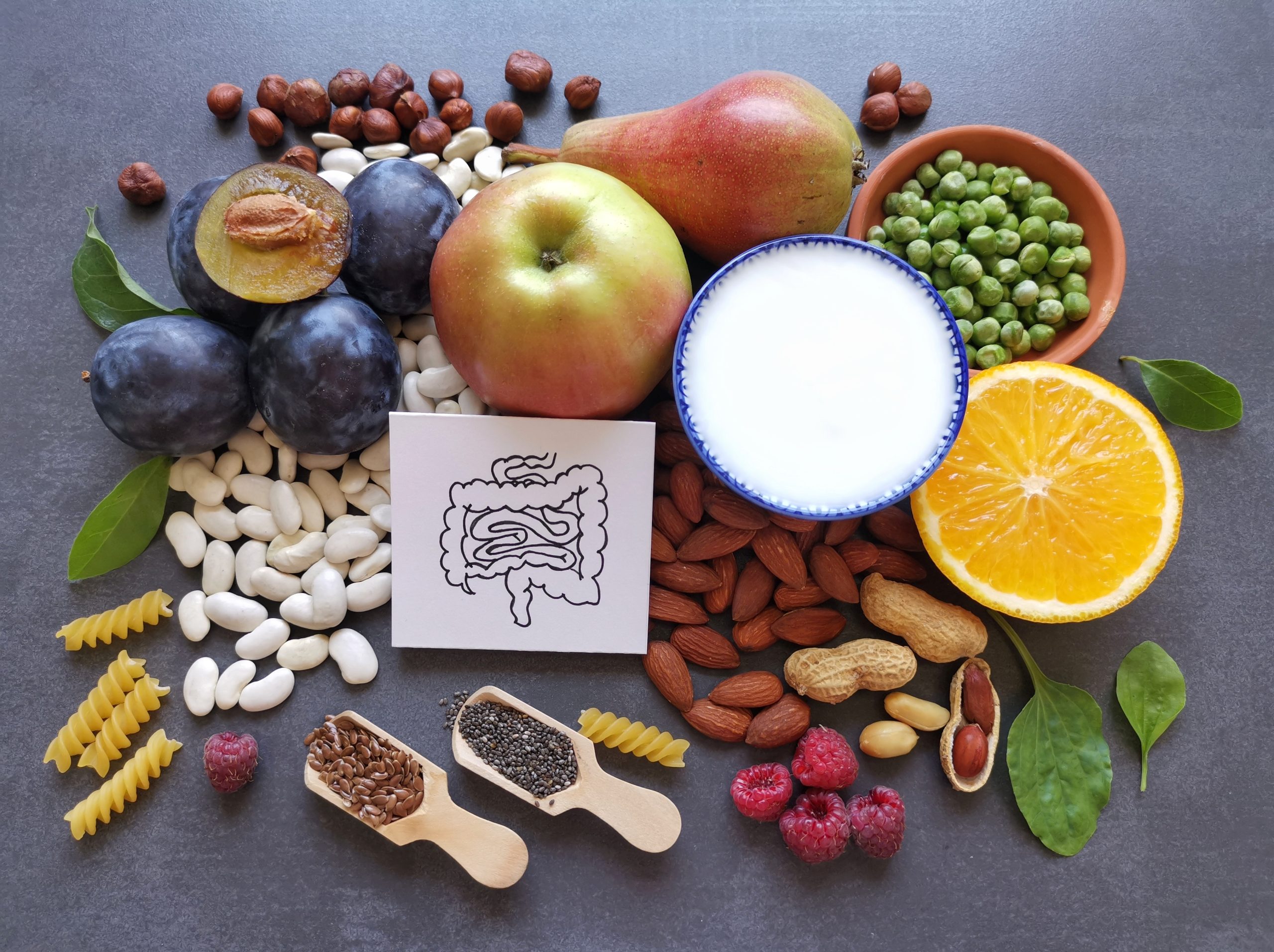
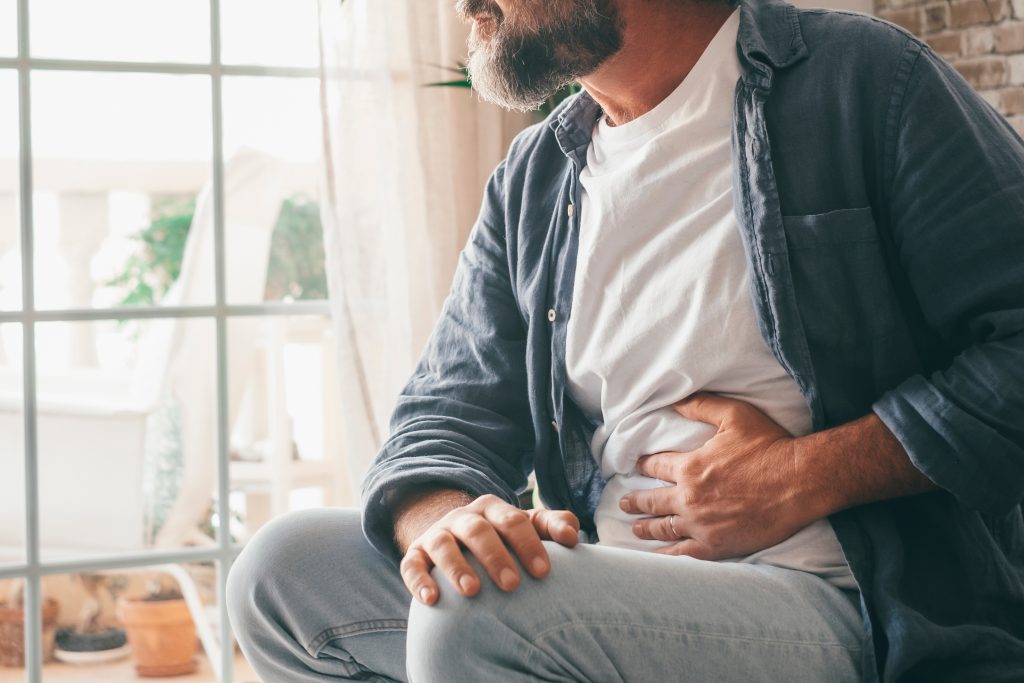
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and other gut health issues are common but often misunderstood digestive disorders. Millions of people worldwide struggle with these conditions, which affect daily life, well-being, and overall health. IBS, in particular, is a chronic digestive disorder that can cause discomfort, bowel movement irregularities, and stress. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments can help sufferers manage these conditions more effectively and improve their digestive health.
IBS is a type of chronic digestive disorder that affects the large intestine. Various gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements often characterize it. There are several subtypes of IBS, including:
- IBS-D: IBS with diarrhea as the primary symptom.
- IBS-C: IBS with constipation as the dominant symptom.
- IBS-M: IBS with alternating diarrhea and constipation.
Although IBS is not life-threatening, it can significantly reduce the quality of life. Gut health issues such as gastrointestinal problems and bowel movement irregularities are commonly associated with IBS. If left untreated, these conditions may cause discomfort, disrupt daily routines, and lead to other health complications.
Common Causes of IBS and Chronic Digestive Disorders
IBS and other digestive disorders are caused by multiple factors, which can vary from person to person. Some of the most common causes include:
- Gut-brain communication issues: In IBS, the interaction between the brain and the gut may be disrupted, leading to altered bowel habits.
- Food sensitivities: Certain foods, such as dairy, gluten, or fatty foods, can trigger IBS symptoms in some individuals.
- Gut infections: A history of bacterial infections or food poisoning can increase the risk of developing IBS.
- Stress and anxiety: Psychological stress can worsen IBS symptoms, as the gut is sensitive to emotional disturbances.
- Overactive histamine system: Patients with IBS have an increased number of Histamine receptors in their GI tract – these can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and urgency when activated.
You can better manage your condition and prevent flare-ups by identifying potential triggers.
Symptoms of IBS and Gastrointestinal Problems
Symptoms of IBS and related gut health issues can vary, but some of the most common include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping: Often relieved after a bowel movement.
- Bloating: Feeling excessively full or gassy.
- Diarrhea or constipation: Frequent bowel movement irregularities are a hallmark of IBS.
- Mucus in stools: A common sign of gastrointestinal distress.
These symptoms can range in severity and frequency, often depending on diet, lifestyle, and stress levels. Chronic digestive disorders like IBS may be ongoing or occur intermittently, making it difficult to predict when symptoms will appear.
How Stress Impacts IBS and Digestive Health
Stress plays a significant role in digestive health and can exacerbate IBS symptoms. The gut and brain are closely linked, with stress and anxiety often leading to increased gut sensitivity, irregular bowel movements, and flare-ups of IBS symptoms. Managing stress is crucial for people with IBS, as reducing anxiety can help improve gut function.
- Worsening of symptoms: Stress can trigger or worsen symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain.
- Increased gut sensitivity: The more stressed you are, the more sensitive your gut becomes, making it more likely to react to triggers like certain foods or emotions.
- Cortisol release: High-stress levels increase cortisol, a hormone that can disrupt digestion and cause discomfort.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and regular exercise can significantly reduce IBS symptoms.
Effective Treatments for IBS and Gut Health
Treatment for IBS and other gut health issues varies based on the severity of symptoms and individual triggers. There are several approaches to managing these conditions.
- Medications: Depending on your symptoms, doctors may recommend anti-diarrheal medications (e.g., loperamide) for IBS-D or laxatives for IBS-C. Antispasmodic drugs like dicyclomine can help alleviate stomach cramping.
- Histamines: Using the right ratio of certain antihistamines to block both the histamine-1 and histamine-2 receptors has shown a great improvement in symptoms. One of the leading examples of this medication is Solamyn, which primarily helps with IBS and IBS-D symptoms – specifically, it has been shown to decrease diarrhea, urgency, bowel irregularity, and abdominal pain.
- Dietary changes: A low FODMAP diet, which eliminates certain carbohydrates known to irritate the gut, is effective for many IBS sufferers. Keeping a food diary can also help identify specific food triggers.
- Probiotics: These supplements promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria, which can help reduce symptoms like bloating and diarrhea.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Since stress plays a significant role in IBS, CBT is effective in helping patients manage stress and reduce symptom flare-ups.
Managing Chronic Digestive Disorders at Home
While medical treatments are available, managing IBS and other chronic digestive disorders often starts at home with simple lifestyle adjustments.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps regulate bowel movements, particularly for those with constipation.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity improves digestion and helps reduce stress, both of which can help relieve IBS symptoms.
- Eat smaller meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help manage IBS symptoms by reducing pressure on the digestive system.
- Track your symptoms: Keeping a symptom journal can help identify patterns and triggers, making it easier to avoid flare-ups.
Foods to Avoid with IBS and Gastrointestinal Problems
Diet plays a major role in managing IBS and gut health issues. Some foods are more likely to trigger symptoms and should be avoided.
- Dairy products: Lactose intolerance is common in IBS sufferers, and dairy can cause bloating and diarrhea.
- Fatty or fried foods can slow digestion and worsen symptoms like constipation and cramping.
- Caffeine and alcohol: Both can irritate the digestive system, leading to diarrhea or constipation.
- Gluten-containing foods: Some IBS sufferers are sensitive to gluten, so avoiding bread, pasta, and baked goods can be helpful.
Natural Remedies for Bowel Movement Irregularities
Many IBS patients seek natural remedies to help manage bowel movement irregularities, which can provide relief without medication.
- Fiber supplements: Soluble fiber, such as psyllium, can help regulate bowel movements and reduce both diarrhea and constipation.
- Peppermint oil: Known for its soothing effect on the gut, peppermint oil can help reduce cramping and bloating.
- Ginger: Ginger tea or supplements can ease nausea and aid digestion.
- Herbal teas: Chamomile and fennel teas are known to calm the digestive system and reduce bloating.
Exploring Gut Health Solutions: Strategies for Long-Term Relief
Improving your gut health is essential for managing IBS in the long term. Incorporating gut health solutions into your daily routine can help maintain balance and reduce symptoms.
- Probiotic-rich foods: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables like sauerkraut contain probiotics, which improve gut health.
- Limit processed foods: Avoid foods high in sugar, fat, and artificial additives, as they can disrupt gut flora.
- Eat fiber-rich foods: Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables promote healthy digestion and help regulate bowel movements.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Gut Health and Alleviate IBS Symptoms
Making simple lifestyle changes can greatly improve your gut health and help alleviate IBS symptoms. Consistency is key to managing chronic digestive disorders.
- Reduce stress: Practice mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to manage stress and reduce gut sensitivity.
- Exercise regularly: Light exercise, like walking or swimming, can improve digestion and lower stress levels.
- Get enough sleep: Poor sleep can disrupt gut health and exacerbate IBS symptoms. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
IBS and gut health issues can be managed with the right combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical treatments. By understanding your symptoms and identifying triggers, you can find relief from chronic digestive disorders and improve your overall digestive health.
The everyday battle of IBS and gut health is not fun, but there are options out there. One of the options that we can offer is Solamyn. Visit Get Relief Rx today to explore proven solutions designed to ease your symptoms and improve your gut health. Click here to start feeling better now!